Networking
Reference:
https://intronetworks.cs.luc.edu/current/html/ipv4.html#special-addresses
回环地址
虽然标准的 IPv4 环回地址是 127.0.0.1,但任何以 127 开头的 IPv4 地址都可以用作环回地址。从逻辑上讲,它们都代表当前主机。大多数主机配置为将名称“localhost”解析为 127.0.0.1。但是,任何环回地址(例如127.255.37.59)都应该可以使用,例如ping. 例如使用 127.0. 1 .0
ipv6 回环地址
在IPv6中,回环地址是0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1,通常被简化为::1
专用地址
专用地址是仅供站点内部使用的 IPv4 地址,例如在 NAT 防火墙后面或根本没有 Internet 连接。如果数据包出现在任何非专用路由器(例如ISP 路由器),并且使用专用 IPv4 地址作为源地址或目标地址,则应丢弃该数据包。定义了三个标准的私有地址块:
- 10.0.0.0/8
- 172.16.0.0/12
- 192.168.0.0/16
最后一个块是 NAT 路由器内置的 DHCP 服务器( 10.3.1 NAT、DHCP 和小型办公室)最常从中分配地址的块。
Example
192.168.0.0/16表示一个CIDR(无类域间路由,Classless Inter-Domain Routing)块。"/16"的含义是前16位是网络部分,剩下的16位是主机部分。
对于这个特定的CIDR块,网络地址是192.168.0.0,广播地址是192.168.255.255。
网络地址和广播地址不能被分配给设备,因此,可用的IP地址范围是从192.168.0.1 192.168.255.254,总共有65,534个
Tip
大多数家庭网络使用 192.168.0.0/16,而大多数公司网络使用其他两个私有地址块之一。
8.1.2.3. IPv6
IPv6固定标头如下图所示;40 字节,是 IPv4 标头大小的两倍。
IPv6 地址
IPv6 地址写成八组,每组四个十六进制数字, 这些组由冒号分隔,并删除了前导 0,例如 fedc:13:1654:310:fedc:bc37:61:3210
如果一个地址包含一长串 0——例如,如果 IPv6 地址有一个嵌入的 IPv4 地址——那么在写入地址时,应该使用字符串“::”来表示创建地址所需的 0000 块正确长度的地址;为避免歧义,这只能使用一次。
举个例子,IPv6地址"2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:ff00:0042:8329"可以被简 为"2001:db8::ff00:42:8329"。
此外,嵌入式 IPv4 地址可能会继续使用“.”。:
::ffff:147.126.65.141
IPv4映射IPv6地址或IPv4兼容IPv6地址
这对于在IPv6环境中逐渐过渡并兼容IPv4环境非常有用
IPv4映射IPv6地址的形式是:0:0:0:0:0:FFFF:IPv4地址。例如,IPv4地址 "192.0.2.47" 映射到IPv6地址会是:"::FFFF:192.0.2.47" 或者是十六进制形式的:"::FFFF:C000:0230"。
8.1.2.4. IPv6 / IPv4 Tunneling
Note that it is possible to tunnel IPv4 through IPv6, IPv6 through IPv4, IPv4 through IPv4 and (last but not least) IPv6 through IPv6, plus using protocols such as teredo and 6to4:
Teredo
- allow IPv4 client access IPv6 client
- use IPv4 udp tunnels
IPV4 head (20byte-60byte/5行-15行)
一行有4个byte
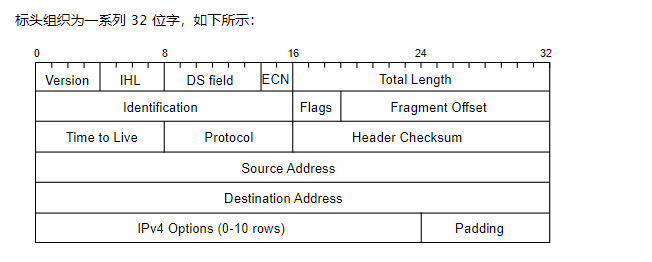
- Version field is, for IPv4, the number 4: 0100
- IHL(4 bits): Internet Header Length, the total IPv4 Header Length, in 32-bit words, points to the beginning of the data. Note that the minimum value for a correct header is 5.
- The IHL field specifies the length of the IPv4 header in units of 32-bit words. Each 32-bit word is equal to 4 bytes (or 4 octets). So, if the IHL field has a value of 5 (which is the minimum for a correct header), that means the length of the header is 5 * 4 bytes = 20 bytes.
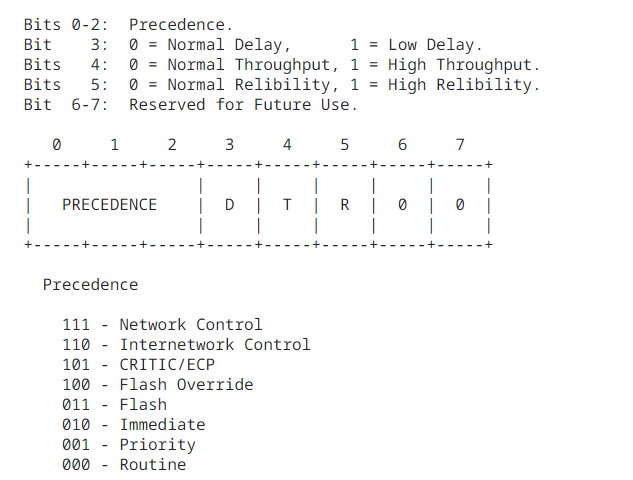
- Type of Service: The Type of Service provides an indication of the abstract parameters of the quality of service desired.
- These parameters are to be used to guide the selection of the actual service parameters when transmitting a datagram through a particular network.
- Several networks offer service precedence, which somehow treats high precedence traffic as more important than other traffic.
Bits 0-2: Precedence.
Bit 3: 0 = Normal Delay, 1 = Low Delay.
Bits 4: 0 = Normal Throughput, 1 = High Throughput.
Bits 5: 0 = Normal Relibility, 1 = High Relibility.
Bit 6-7: Reserved for Future Use.
- Total Length(16 bits): including internet header and data.
- Identification (16 bits): An identifying value assigned by the sender to aid in assembling the fragments of a datagram.
- Flags: 3 bits
Bit 0: reserved, must be zero
Bit 1: (DF) 0 = May Fragment, 1 = Don't Fragment.
Bit 2: (MF) 0 = Last Fragment, 1 = More Fragments.
- Fragment Offset(13 bits): This field indicates where in the datagram this fragment belongs.
- Time to Live
- Protocol(8 bits): This field indicates the next level protocol used in the data portion of the internet datagram. If you are using TCP (Transmission Control Protocol), the value of the Protocol field will be 6.
- Header Checksum (16 bit)A checksum on the header only. Since some header fields change(e.g., time to live), this is recomputed and verified at each point that the internet header is processed
- 让我们用一个简化的例子来演示校验和的计算。为简单起见,我们假设一个 IP 报头只有两个 16 位字(实际上,它要大得多)
#假设我们的标头是(二进制):
Word 1: 1100110011001100
Word 2: 1010101010101010
#计算的第一步是对单词求和:
1100110011001100 (Word 1)
+
1010101010101010 (Word 2)
----------------
1011101110110110 (sum)
#然后我们计算和的补码,这只是简单地翻转所有位:
1011101110110110 (sum)
becomes
0100010001001001 (one's complement)
#这个补码是放在 IP 标头中的校验和字段中的内容。当接收到数据包时,接收方对报头执行相同的操作(这次包括接收到的校验和值)。如果标头没有错误,这将导致所有 1 的总和,并且其补码将全为 0
- Source Address
- Destination Address
- Options
- Padding
Network Address Translation(NAT)
如果您的 ISP 分配给您一个 IPv4 地址并且您有两台计算机,您会怎么做?
NAT 能够在单个 IPv4 地址(或少量地址)后面“多路复用”任意数量的单个主机,这使其成为保护 IPv4 地址的重要工具。
但是,它也启用了一种重要形式的基于防火墙的安全性。它记录在RFC 3022,这里称为 NAPT,或网络地址端口转换。另一个常用术语是IP 伪装。
基本思想是,不是为站点上的每台主机分配一个公开可见的 IPv4 地址,而是将一个这样的地址分配给称为 NAT 路由器的特殊设备。用于住宅或小型办公室的 NAT 路由器通常简称为“路由器”,或(更准确地说)“住宅网关”。NAT路由器的一侧连接到互联网;另一个连接到站点的内部网络。内部网络上的主机分配有专用 IP 地址(见专用地址)
当一台内部机器想要连接到外部时,NAT 路由器拦截连接,并在重写源地址后转发连接的数据包,使其看起来像是来自 NAT 路由器自己的 IP 地址,如下所示为 200.1.2.37。
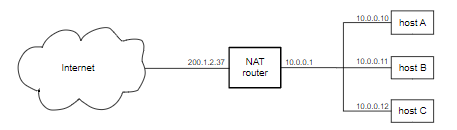
远程机器响应,将其响应发送到 NAT 路由器的公共 IPv4 地址。NAT 路由器记住连接,将连接信息存储在一个特殊的转发表中,并将数据转发到正确的内部主机,重写传入数据包的目标地址字段。

Sometimes it is necessary for the NAT router to rewrite the internal-side port number as well; this happens if two internal hosts want to connect, each from the same port, to the same external host and port.
example, suppose B now opens a connection to ⟨S,80⟩, also from inside port 3000. This time the NAT router must remap the port number, because that is the only way to distinguish between packets from ⟨S,80⟩ back to A and to B. With B’s second connection’s internal port remapped from 3000 to 3001, the new table is
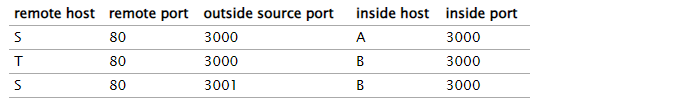
NAT 路由器不在它自己和外部主机之间创建 TCP 连接;它只是转发数据包(重写)。连接端点仍然是外部主机 S 和 T 以及内部主机 A 和 B。但是,NR 可能会很好地监视TCP 连接以了解它们何时关闭(通过查找 FIN 数据包,17.8.1 关闭连接),所以可以从表中删除。对于 UDP 连接,NAT 路由器通常会在一段时间不活动后删除转发条目;参见16 UDP 传输,练习 16.0。
Mobile IP
a mobile host has a permanent home address and, while roaming about, will also have a temporary care-of address, which changes from place to place. The care-of address might be, for example, an IP address assigned by a local Wi-Fi network, and* which in the absence of Mobile IP would be the IP address for the mobile host.在没有移动 IP 的情况下,它将是移动主机的 IP 地址*
The goal of Mobile IP is to make sure that the mobile host is always reachable via its home address.
To maintain connectivity to the home address, a Mobile IP host needs to have a home agent back on the home network; the job of the home agent is to maintain an IP tunnel that always connects to the device’s current care-of address.
IP-in-IP Encapsulation
used for Mobile IP tunneling
In this process, the entire original IP packet (with header addressed to the home address) is used as data for a new IP packet, with a new IP header (the “outer” header) addressed to the care-of address.

A value of 4 in the outer-IP-header Protocol field indicates that IPv4-in-IPv4 tunneling is being used, so the receiver knows to forward the packet on using the information in the inner header.
The MTU of the tunnel will be the original MTU of the path to the care-of address, minus the size of the outer header.
TCP
TCP和IP的关系
简而言之,IP 负责将数据包从一个节点移动到另一个节点。TCP 负责验证从客户端到服务器的数据传送是否正确。数据可能会在网络中丢失,但 TCP 会处理并重新传输丢失的数据。
IP 是一种网络层协议,负责通过 Internet 将数据包从源路由到目的地。它是一种无连接协议,这意味着它在发送数据之前不会建立连接,也不保证数据包一定会到达目的地,或者它们会按照发送的顺序到达。
另一方面,TCP 在传输层运行并提供使互联网连接可靠的服务。它在发送数据之前建立连接,确保数据到达目的地,检查错误,并确保数据包以正确的顺序放置。TCP 通过向每个数据包添加一个标头来实现这一点,其中包含包含序列号和校验和的信息。
给我一个例子来说明tcp如何使用ip?
当您请求网页时,您的浏览器(客户端)需要向托管www.example.com 的服务器发送请求。这是使用 TCP/IP 完成的。
以下是对所涉及步骤的简化说明:
- TCP 连接建立(三次握手):您的计算机首先与服务器建立 TCP 连接。它发送一个设置了 SYN(同步)标志的 TCP 数据包。这就像在说,“嗨,服务器,我想与你建立连接。”
- 服务器使用设置了 SYN 和 ACK(确认)标志的 TCP 数据包进行响应。这是服务器在说,“嗨,客户,我收到了你的请求,我也准备好建立连接了。”
- 然后您的计算机发送另一个设置了 ACK 标志的 TCP 数据包。这样就完成了握手并建立了连接。您的计算机现在正在说:“太好了,我收到了您的回复,我们的连接已建立。”
- 数据传输:建立连接后,您的计算机可以通过此 TCP 连接发送网页的 HTTP 请求。请求被分解为 TCP 数据包。然后将这些数据包封装在 IP 数据包中,因为 TCP 不关心或不知道路由细节。IP 层处理这些数据包在 Internet 上的路由。
- IP 数据包在 Internet 上传输,可能通过许多路由器和不同的网络,直到它们到达服务器。服务器上的 IP 层然后从 IP 数据包中解压缩 TCP 数据包。
- 服务器上的 TCP 层获取数据包,确保它们都在那里并以正确的顺序(使用 TCP 标头中的序列号),并将数据向上传递到 HTTP 服务器。
- 数据接收和确认:服务器向客户端发送确认接收到的数据包。这是 TCP 可靠性功能的一部分。
- 然后服务器响应 HTTP 请求,使用相同的 TCP/IP 进程将网页数据发送回您的计算机。
- TCP 连接终止(四次握手):发送完所有网页数据后,服务器将发送一个设置了 FIN(完成)标志的 TCP 数据包。这就像在说,“我已经把这个请求的所有数据都发给你了。” 您的计算机以 ACK 响应,然后在发送完所有剩余数据后也发送 FIN 数据包。服务器用 ACK 响应 FIN,连接关闭。
TCP 机制
reference: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc793#section-3.1
TCP 头
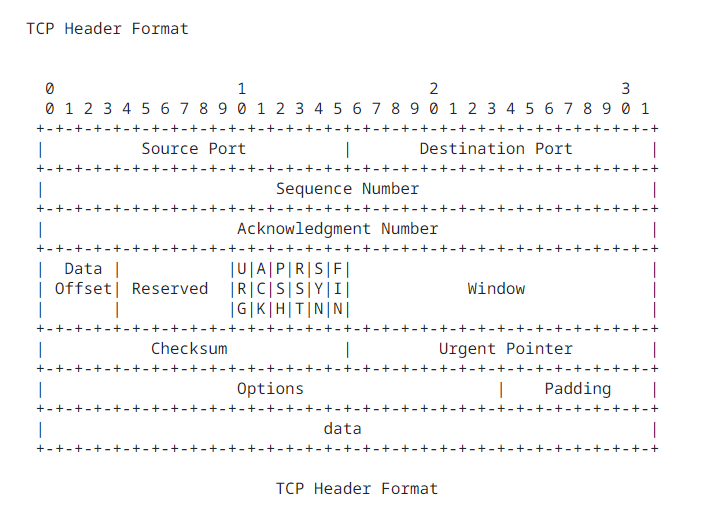
- Source Port: (16 bits) The source port number.
- Destination Port: (16 bits) The destination port number.